Data Fetching in Next.js
Next.js offers different methods to fetch data for your page content - choosing the right approach for your application will allow you to benefit from the performant advantages that Next.js provides. We will first start with describing the different methods available, followed with an e-commerce use-case example.
Static Site Generation vs Server-side Rendering
Static Rendering
Your pages are generated as static HTML and this is done at compilation time. It is then served to your users when they request your page.
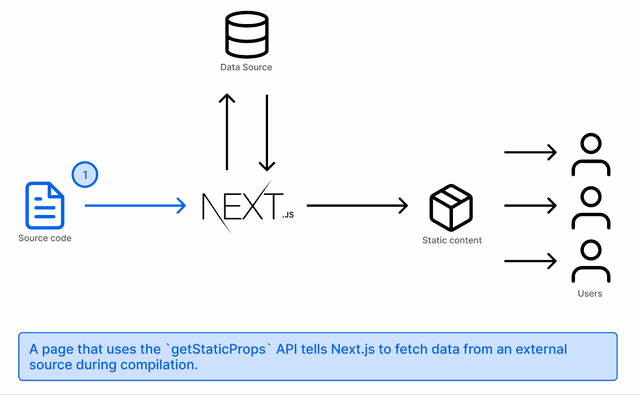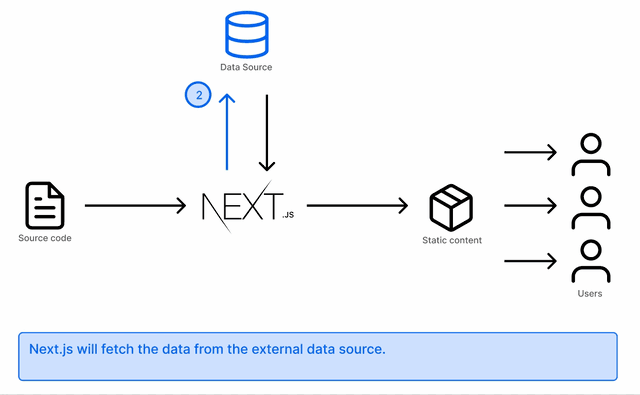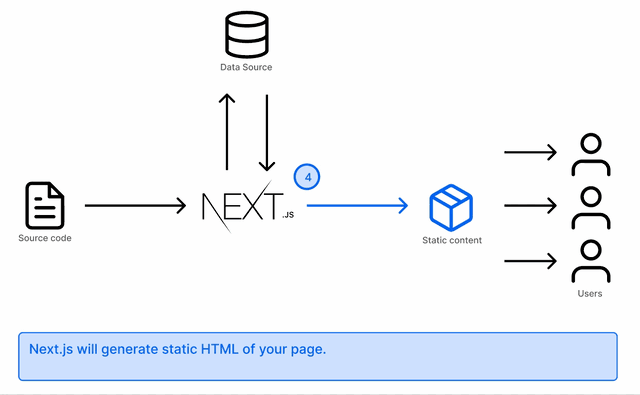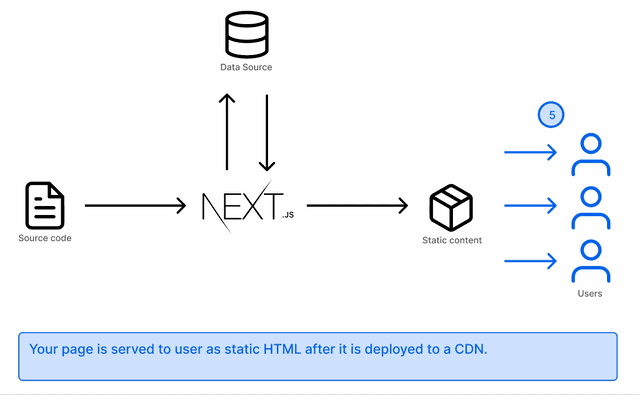
This is done by using the getStaticProps API. If Next.js finds a page using only this API to fetch data, it will pre-render the page at build time using the props returned from this API.
The content can be cached and served from a CDN. The advantages of this approach:
- Very performant - no server required to render content.
- Always available - no need for a database when user requests the page.
- Less load on backend services - the backend is only required during compilation.
Although, because the content is generated ahead of time, it can be outdated and requires additional deployments to refresh the content.
Server-side Rendering
When a user requests a page, Next.js will generate the content on the server and return it to the user. This is done on per request.
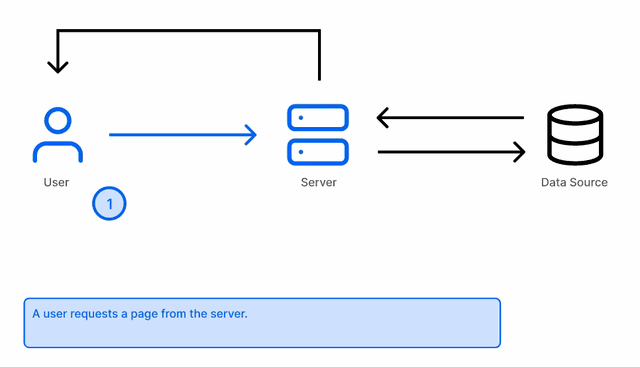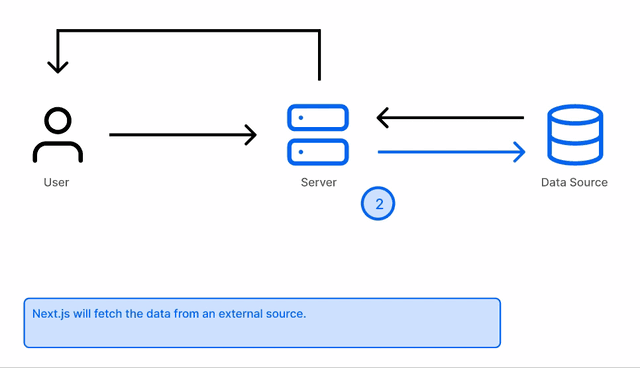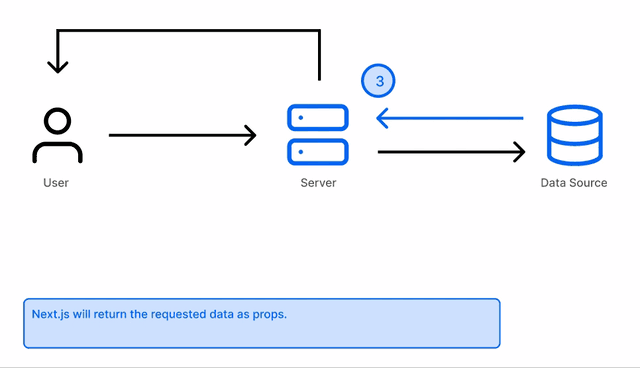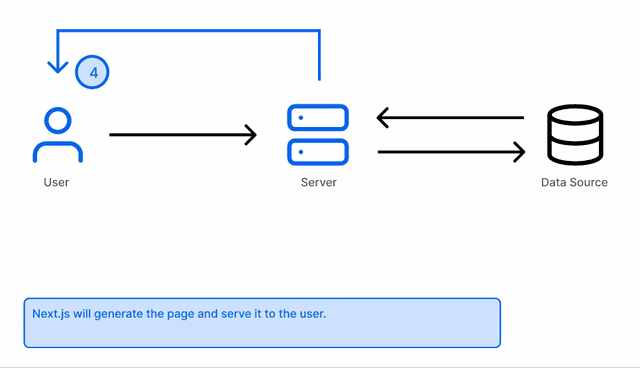
Next.js will enable Server-side rendering when the getServerSideProps API is used in a page.
Additional deployments are not necessary and the user will always get the latest content because the server will be ready to take in requests and generate the content, but the page will lose the benefits of static site generation and it will have the added processing time required to build the page on the server.
Use Case: E-commerce
You can configure each page of your application to fetch data differently. Let’s take an e-commerce app as an example:
Product Catalog Page: Static generation
A product listing page will require a list of all available products. We can use getStaticProps to generate a static HTML page and Next.js can fetch the content from an external data source during build time.
export async function getStaticProps() {
return {
props: {
products: await getProducts()
}
};
}
const Products = ({ products }) => {
return (
<section>
<h1>Products</h1>
<ul>
{products.map((product) => (
<li key={product.id}>{product.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</section>
);
};
export default Products;Product Detail Page: Static generation with dynamic routes
We need a page for each product and for us to do this, we will use getStaticPaths to return a list of product IDs. For each product ID, we will generate a static product page:
Create a page page/products/[id].js which uses dynamic routes.
// Pre-render the path of each product
export async function getStaticPaths() {
const products = await getProducts();
const paths = products.map((product) => ({
params: { id: product.id }
}));
return { paths };
}
// Pre-render the page with data related to each product
export async function getStaticProps({ params }) {
return {
props: {
product: await getProduct(params.id)
}
};
}
const Product = ({ product }) => {
return (
<section>
<h1>{product.name}</h1>
</section>
);
};
export default Product;Shopping Cart: Static generation + client-side fetching
The content on a shopping cart is different for each user, we can render the page layout as static content and then load the client-side data in the browser:
const ShoppingCart = () => {
const { data } = useSWR('/api/cart', fetchCart);
return (
<section>
<h1>Your Cart</h1>
<ul>
{data.products.map((product) => (
<li key={product.id}>{product.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
</section>
);
};
export default ShoppingCart;The above example uses SWR to handle the data fetching.
Conclusion
Next.js supports different ways to fetch data, with static site generation having the advantages required for a fast page load experience. Take the load off the browser rendering your content and prepare it ahead of time during compilation time.
This approach is demonstrated with projects such as Go Bare, an e-commerce website that fetches the content from Shopify and builds the static HTML content. The user is viewing content served from a CDN, rather than requesting it directly from Shopify. When the user is at the shopping cart, we do a client side fetch to Shopify to request data related to the shopping cart session.